Involves informal agreements with verbal understandings between the buyer and seller, often including specific due dates and late payment fees. Written promises made by the borrower to the lender, stating a borrower’s payment obligation to the lender on a specified date. To help you do that, we will cover everything about notes payable in this article. You’ve already made your original entries and are ready to pay the loan back. Recording these entries in your books helps ensure your books are balanced until you pay off the liability.
Top 10 Proven Tips For Automating Your Cash Application Process
This is because such an entry would overstate the acquisition cost of the equipment and subsequent depreciation charges and understate subsequent interest expense. Therefore, in reality, there is an implied interest rate in this transaction because Ng will be paying $18,735 over the next 3 years for what it could have purchased immediately for $15,000. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Looking for ways to streamline and get clearer insights into your AP and AR? BILL’s financial automation can help you do both and free up bandwidth to focus on your core mission.
What is your current financial priority?
The contracts must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), being identified as a security sometimes. Notes payable on the balance sheet take a spot under the liabilities column. They are considered current liabilities when the amount is due within one year, and else they are recorded under the long-term liabilities category. The organization borrows money from the owner of the firm, and the borrower agrees to repay the amount borrowed plus interest at a specified date in the future. As the notes payable usually comes with the interest payment obligation, the company needs to also account for the accrued interest at the period-end adjusting entry. This is due to the interest expense is the type of expense that incurs through the passage of time.
Notes Payable on a Balance Sheet
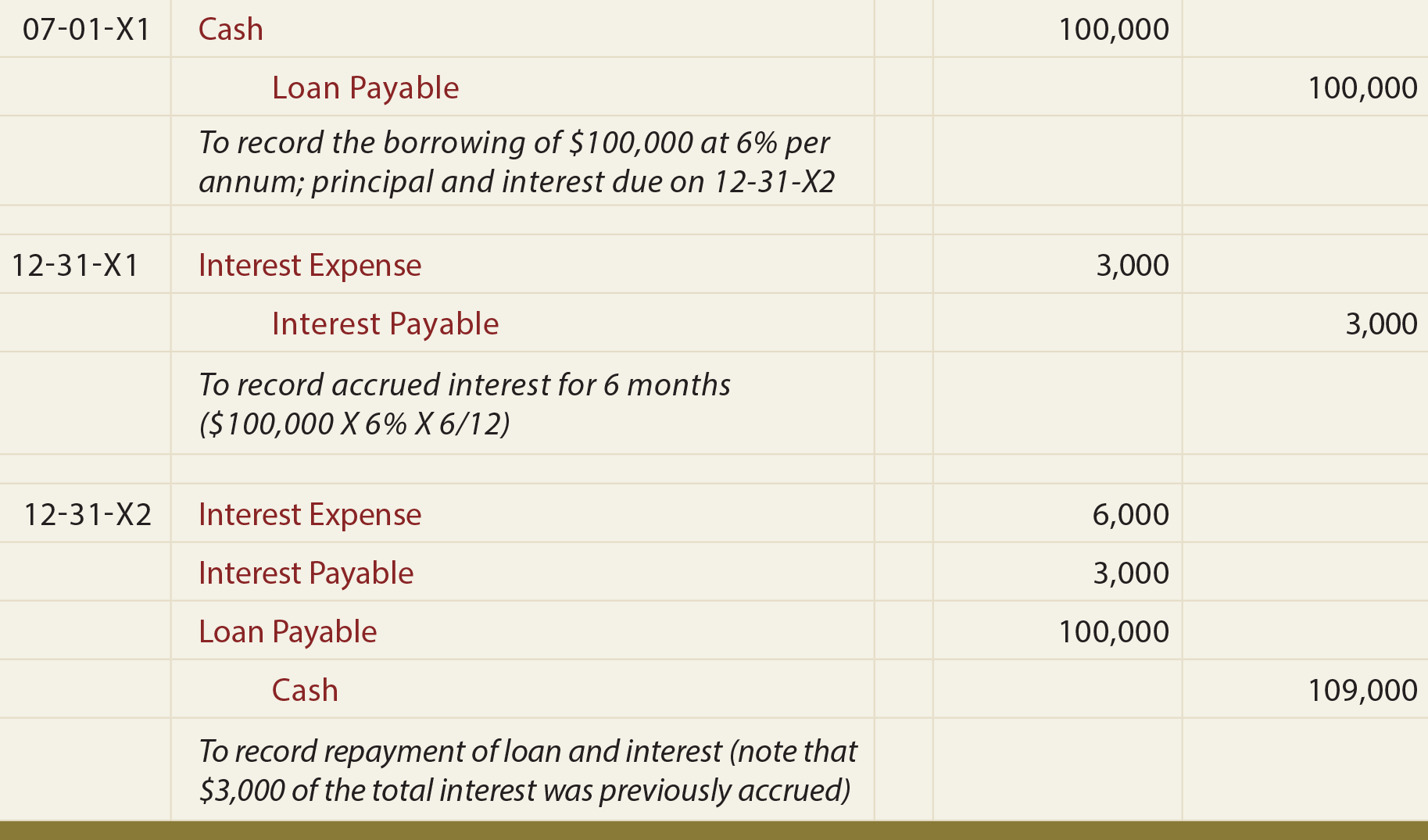
When the company makes the payment on the interest of notes payable, it can make journal entry by debiting the interest payable account and crediting the cash account. A small manufacturing company needs additional funds to expand its operations. It approaches a bank and takes out a $50,000 loan, agreeing to repay it with interest over three years.
What Is Notes Payable, and How Do You Record Them in Your Books?
These require users to share information like the loan amount, interest rate, and payment schedule. For example, a business borrows $50,000 at an interest rate of 5 percent per year, with a schedule to pay the loan amount back in 60 monthly installments. Consider them carefully when negotiating the terms of a note payable. As the loan will mature and be payable on the due date, the following entry will be passed in the books of account for recording it. Let’s look at what entries are passed in the journal for notes payable. Here are some examples with journal entries involving various face value, or stated rates, compared to market rates.
Both accounts payable and notes payable share the common aspect of being payable in nature, meaning they involve debts that a company must pay to settle its obligations. An interest-bearing note payable may also be issued on account rather than for cash. In this case, a company already owed for a product or service it previously was invoiced for on account. Rather than paying the account off on the due date, the company requests an extension and converts the accounts payable to a note payable. In your notes payable account, the record typically specifies the principal amount, due date, and interest.
Are known, the fifth unknown variable amount can be determined using a financial calculator or an Excel net present value function. For example, if the interest rate (I/Y) is not known, it can be derived if all the other variables in the variables string are known. This will be illustrated when non-interest-bearing long-term notes payable are discussed later in this chapter. As the length of time to maturity of the note increases, the interest component becomes increasingly more significant. As a result, any notes payable with greater than one year to maturity are to be classified as long-term notes and require the use of present values to estimate their fair value at the time of issuance. A review of the time value of money, or present value, is presented in the following to assist you with this learning concept.
The impact of promissory notes or notes payable appears in the company’s financial statements. For the first journal entry, you would debit your cash account with the loan amount of $10,000 since your cash increases once the loan has been received. is notes payable an asset Notes payable differ from accounts payable because they involve a formal written agreement with specific terms, including interest rates and maturity dates. In contrast, accounts payable are debts owed to suppliers for goods or services received.
- The notes payable are not issued to general public or traded in the market like bonds, shares or other trading securities.
- Though choosing this option helps people refrain from paying more as interest when inconvenient, the same adds up to the total amount to be repaid in the long run, increasing the burden.
- Accounts payable represents the amount a company owes its suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit.
- In this journal entry, interest expenses is a debit entry, and interest payable is a credit entry, as a portion of it is yet to be paid.
- F. Giant must pay the entire principal and, in the first case, the accrued interest.
- The proper classification of a note payable is of interest from an analyst’s perspective, to see if notes are coming due in the near future; this could indicate an impending liquidity problem.
A troubled debt restructuring occurs if a lender grants concessions such as a reduced interest rate, an extended maturity date, or a reduction in the debts’ face amount. These can take the form of a settlement of the debt or a modification of the debt’s terms. Notes payable are initially recognized at the fair value on the date that the note is legally executed (usually upon signing). Subsequent valuation is measured at amortized cost using the effective interest rate. By leveraging AR automation, you can reduce human intervention in generating invoices, sending payment reminders, and reconciling payments. Can impact working capital, especially if they are short-term liabilities, which can be used to estimate current working capital.
Also, the process to issue a long-term note is more formal, and involves approval by the board of directors and the creation of legal documents that outline the rights and obligations of both parties. These include the interest rate, property pledged as security, payment terms, due dates, and any restrictive covenants. Restrictive covenants are any quantifiable measures that are given minimum threshold values that the borrower must maintain.
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. These obligations generally have shorter payment terms, usually within 30 to 90 days.Terms can be longer for large ticket items, custom products or on export transactions. Notes payable include terms agreed upon by both parties—the note’s payee and the note’s issuer—such as the principal, interest, maturity (payable date), and the signature of the issuer. On June 1, Edmunds Co. receives a $30,000, three-year note from Virginia Simms Ltd. in exchange for some swamp land. The land has a historic cost of $5,000 but neither the market rate nor the fair value of the land can be determined.

